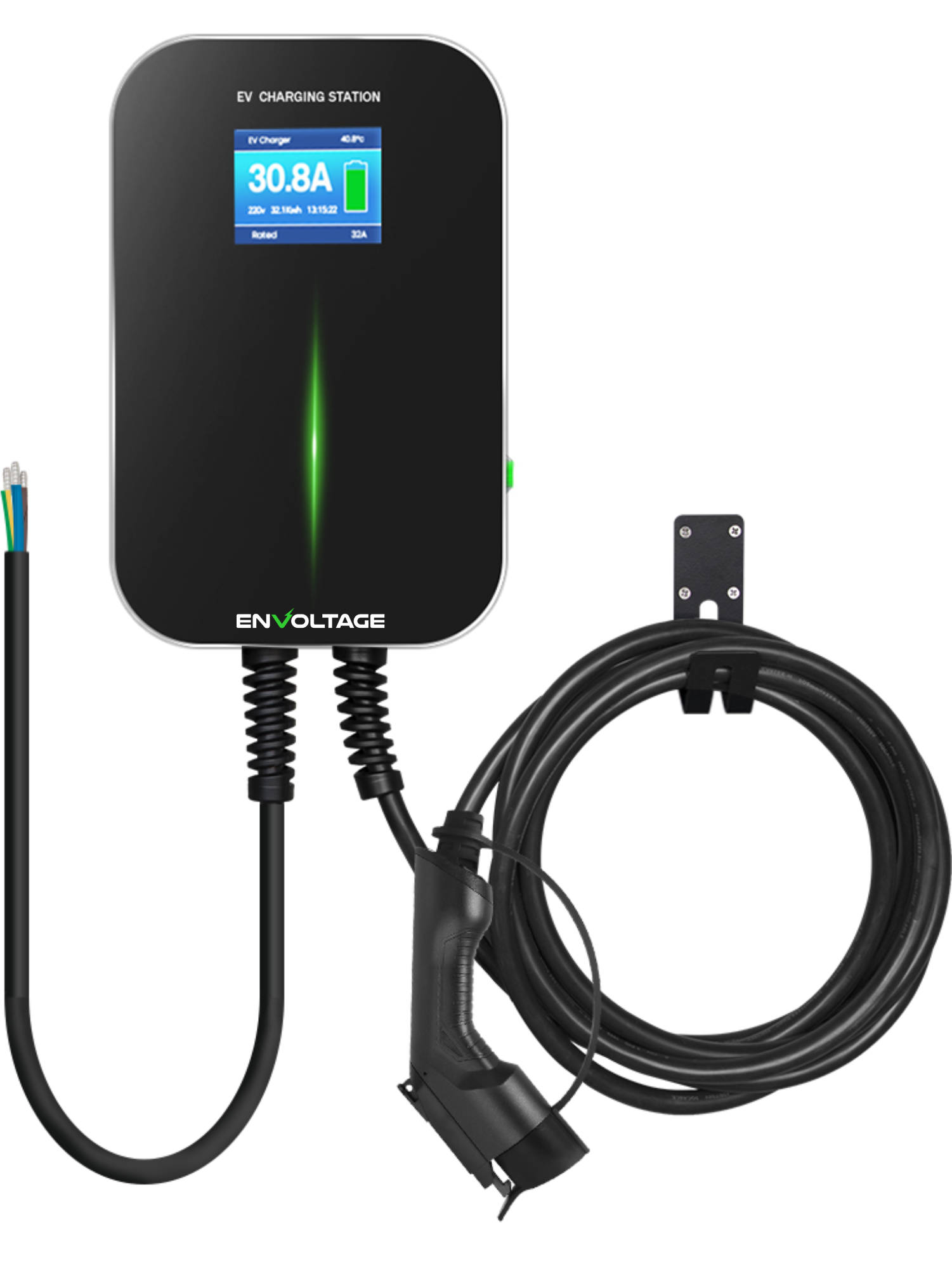
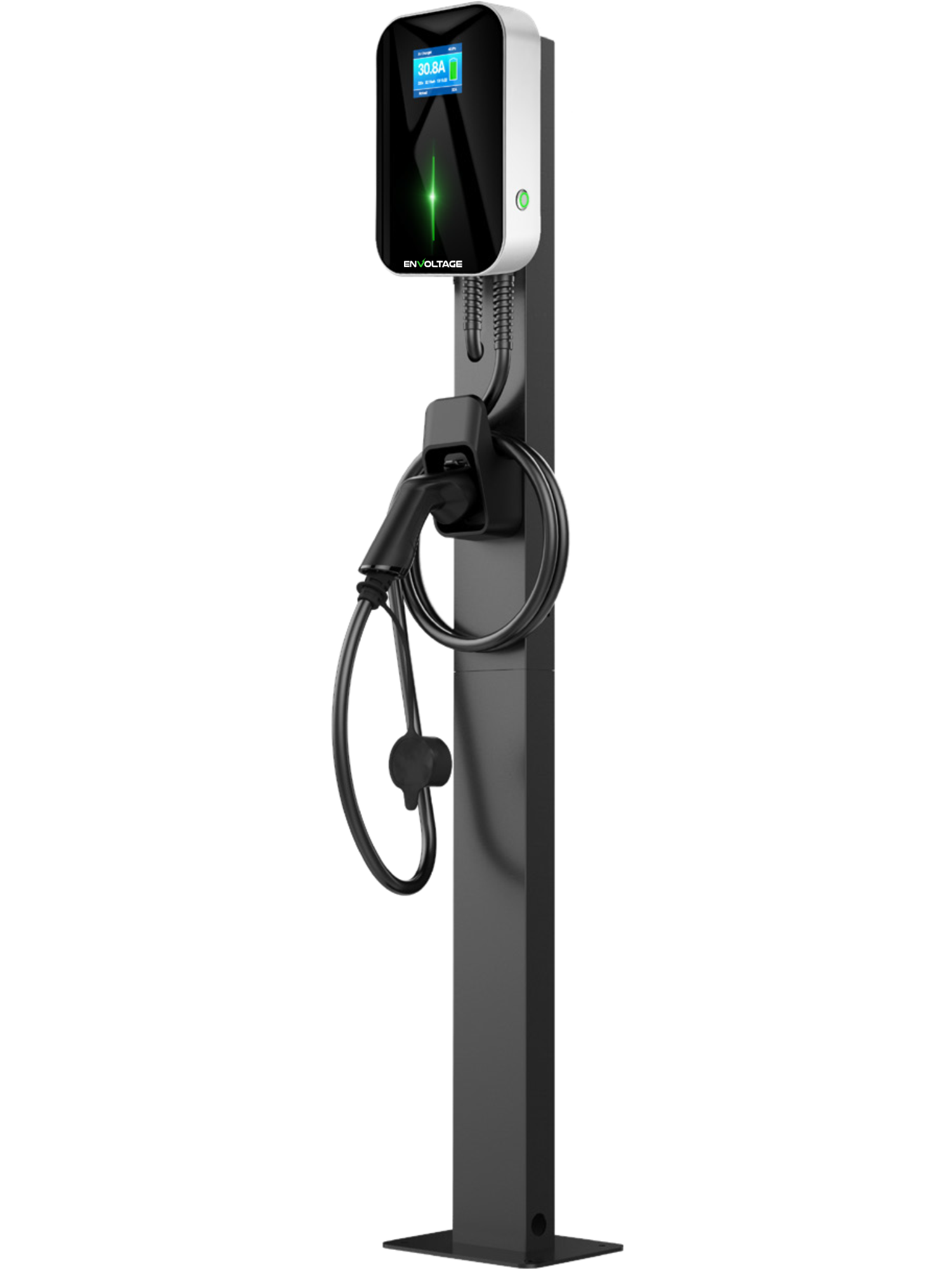
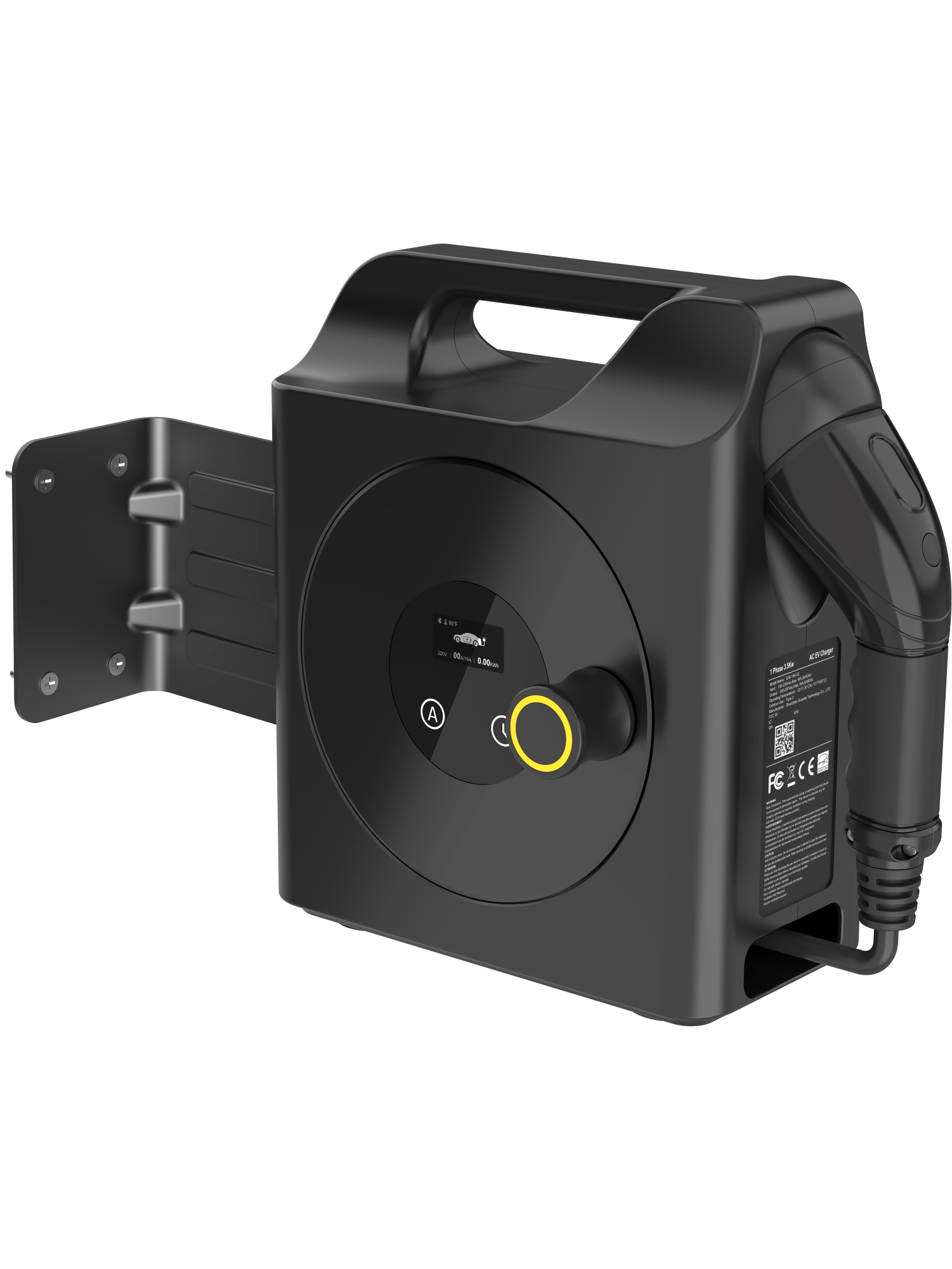
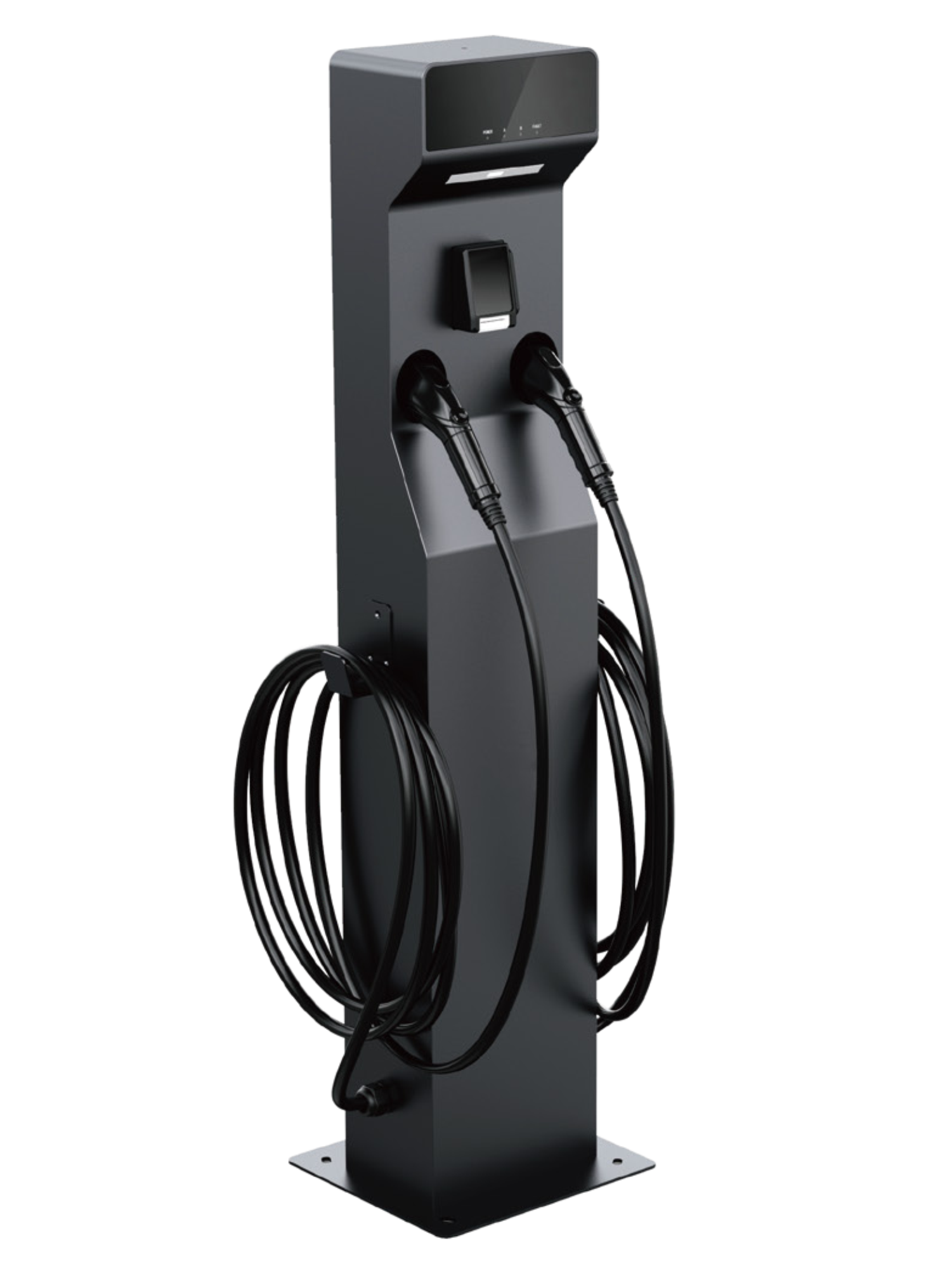
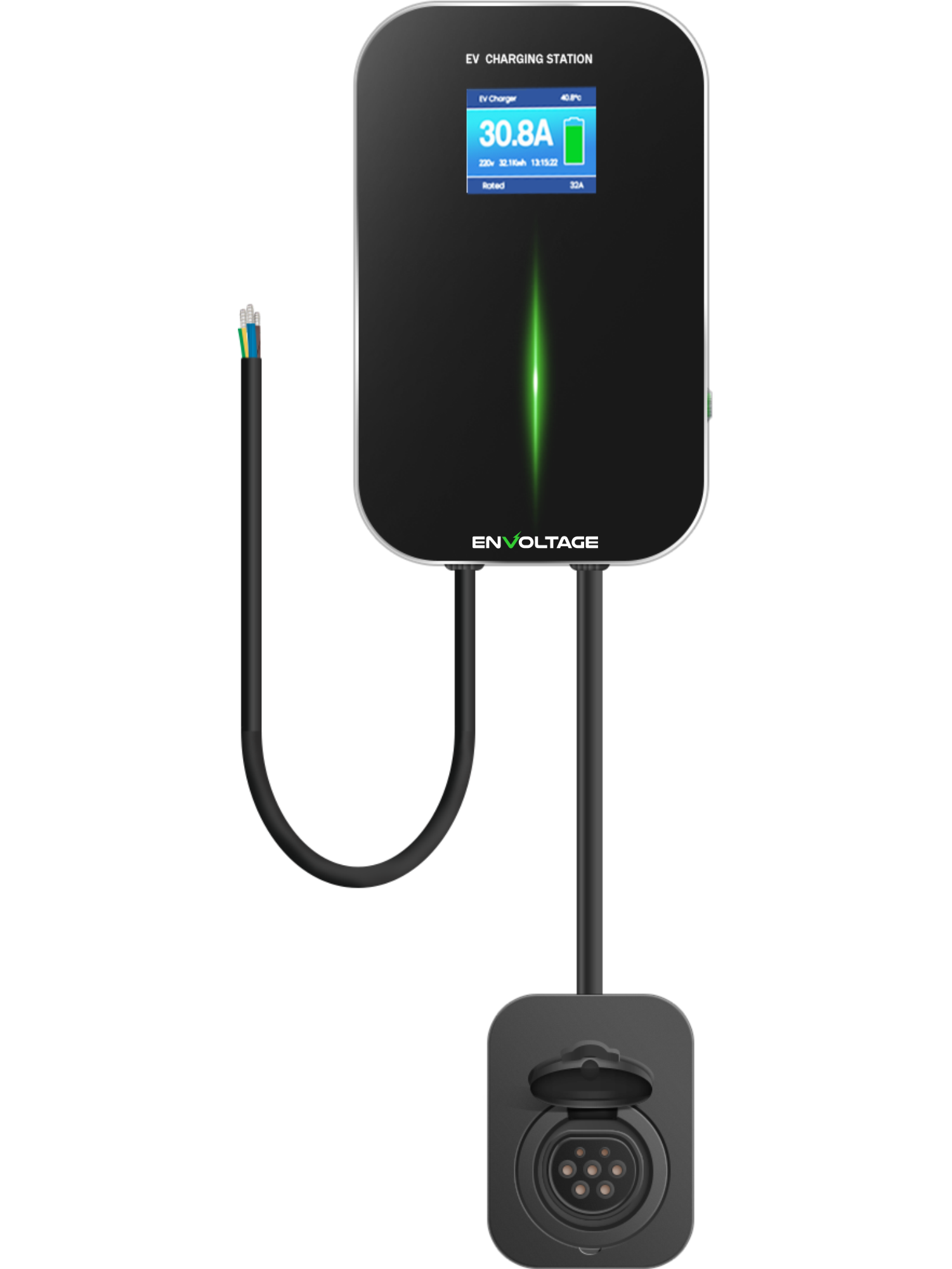
EV Chargers are suitable for residential and commercial use. They are easy to install, stable in performance, and have a complete protection mechanism. The LCD display can show the detailed charging status. Available with plugs for all EV makes and models, IP66 environmental protection and support control by RFID/APP/OCPP/Wi-Fi. Advanced features include automatic temperature monitoring, smart chip auto-repair faults and Type A + 6mA leakage protector.
Level 3 Fast Chargers
Level 2 Chargers
Get a Quote / Learn More
Have questions or need help? Use this form to reach out and we will be in touch with you as quickly as possible.
Electric Vehicle (EV) Chargers and Charging Systems
Welcome to our knowledge base on Electric Vehicle (EV) Chargers and Charging Systems.
EV chargers are the critical link between your power source — whether it’s the grid, solar panels, or an energy storage system — and your electric vehicle.
Understanding the types, features, and installation requirements of EV chargers helps you choose the right solution for residential, commercial, and industrial applications.
What Is an EV Charger?
An EV charger, also called Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment (EVSE), safely delivers electrical power from a source to an electric vehicle’s onboard battery.
It regulates voltage, monitors current, and communicates with the vehicle to ensure a safe and efficient charge.
EV chargers can be connected to:
- The electrical grid
- A solar + storage system
- Or a microgrid in off-grid or commercial setups
Modern EV chargers also include smart energy management, load balancing, and connectivity features for billing or remote control.
How EV Charging Works
When you plug in an EV:
- The charger communicates with the vehicle’s onboard charger.
- Power flow begins only after a safe connection is verified.
- The onboard charger converts AC to DC to charge the battery (for Level 1 & 2).
- In DC fast charging, the charger itself converts AC to DC and feeds the battery directly.
This controlled process ensures safe voltage, current, and temperature levels throughout the charging session.
Types of EV Chargers
EV chargers are categorized by power level, charging speed, and connection type.
1. Level 1 Chargers (120V AC)
Overview:
Level 1 chargers plug directly into a standard household outlet. They’re the simplest and slowest type of charger, typically included with most electric vehicles.
Charging Speed:
2–5 miles of range per hour
Advantages:
- No special installation required
- Ideal for overnight home charging
- Low cost
Limitations:
- Very slow charging rate
- Not suitable for high-capacity EVs
Best For:
Homeowners with low daily driving needs or plug-in hybrids.
2. Level 2 Chargers (208–240V AC)
Overview:
Level 2 chargers are the most common choice for residential, commercial, and workplace installations.
They require a 240V circuit and can deliver significantly faster charging than Level 1.
Charging Speed:
10–60 miles of range per hour (3.3 kW–19.2 kW output)
Advantages:
- Fast charging for daily use
- Smart features (Wi-Fi, app control, scheduling)
- Compatible with solar and battery integration
- Ideal for shared or fleet environments
Limitations:
- Requires professional installation
- Higher cost than Level 1
Best For:
Homes, businesses, fleets, and parking facilities.
3. DC Fast Chargers (Level 3 / 400V–1000V DC)
Overview:
DC fast chargers (DCFC) bypass the vehicle’s onboard AC charger, supplying DC power directly to the battery.
They are designed for commercial, industrial, and public charging stations.
Charging Speed:
Up to 250–350 kW (80% charge in 15–45 minutes)
Advantages:
- Ultra-fast charging for long-distance travel
- Network-enabled for public and fleet use
- Scalable for multi-station setups
Limitations:
- High installation and equipment cost
- Requires three-phase or high-voltage power
- May reduce battery longevity with frequent use
Best For:
High-traffic public charging sites, fleets, and commercial facilities.
Connector Types
Different EVs use different plug types depending on region and manufacturer:
- J1772 (Type 1): Common for Level 1 and Level 2 charging in North America
- Type 2 (Mennekes): Standard in Europe
- CCS (Combined Charging System): Used for DC fast charging (North America & Europe)
- CHAdeMO: Used by some Asian manufacturers (e.g., Nissan Leaf)
- NACS (Tesla): Tesla’s proprietary connector, becoming more widely adopted
Smart Charging and Energy Integration
Modern EV chargers can connect with solar panels, energy storage systems, and smart home energy management tools.
Key Smart Features Include:
- Scheduled or off-peak charging
- Dynamic load balancing across multiple chargers
- Integration with solar and battery systems
- App-based monitoring and control
- Usage data and billing reports for fleets or tenants
- OCPP (Open Charge Point Protocol) communication compatibility
Smart charging enables cost savings, renewable energy optimization, and grid-friendly load management.
EV Charger Installation Considerations
When planning an EV charger installation, consider:
- Power Supply: Single-phase (residential) or three-phase (commercial/industrial)
- Circuit Capacity: Sufficient amperage and breaker size
- Location: Accessibility, weather protection, and cable reach
- Mounting Type: Wall-mounted, pedestal, or portable
- Connectivity: Wi-Fi, Ethernet, or cellular communication options
- Permitting: Local electrical codes and inspection requirements
For Level 2 or DC fast chargers, installation should always be performed by a licensed electrician or certified EVSE installer.
Safety and Standards
All EV chargers must meet strict safety and performance standards, including:
- UL 2594 / UL 2231: Safety standards for EV charging equipment
- NEC Article 625: U.S. electrical code for EV charging systems
- IEC 61851 / 62196: International standards for connectors and operation
- SAE J1772: Communication protocol and connector standards
Modern chargers include built-in protection against:
- Overcurrent and short circuit
- Ground fault detection
- Overtemperature
- Power surge and voltage irregularities
Maintenance and Monitoring
EV chargers are generally low-maintenance but benefit from routine checks:
- Inspect for cable wear or connector damage
- Keep ventilation and cable areas clean
- Update firmware periodically
- Review usage logs for performance monitoring
Cloud-connected chargers provide real-time diagnostics and remote troubleshooting, minimizing downtime for commercial applications.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I charge my EV from solar panels or a battery system?
Yes — when paired with a solar inverter or energy storage system, you can charge your EV using stored or renewable energy.
Do I need a special outlet for a Level 2 charger?
Yes, a 240V circuit (similar to an electric dryer outlet) is required for Level 2 charging.
Can all EVs use DC fast chargers?
Most modern EVs support DC fast charging, but connector types and charging speeds vary by model.
Is smart charging worth it for homeowners?
Absolutely. Smart chargers let you control charging times, lower energy costs, and integrate renewable power.